Difference between revisions of "Capsis"
(→Brief overview) |
Ola Eriksson (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== General System description == | == General System description == | ||
| − | System name: Capsis - '''C'''omputer '''A'''ided '''P''' | + | System name: Capsis - '''C'''omputer '''A'''ided '''P'''rojection of '''S'''trategies '''I'''n '''S'''ilviculture |
Acronym: Capsis | Acronym: Capsis | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Category:Decision support system]] | [[Category:Decision support system]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:French DSS]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Brief overview === | === Brief overview === | ||
| − | [[Capsis]] is a software platform which purpose is to host forestry growth and yield / | + | [[Capsis]] is a software platform which purpose is to host forestry growth and yield / dynamics models. It can help run various silvicultural scenarios by combining a given growth model with silvicultural treatments. It was built by french researchers (INRA, France) for forest research (hypotheses testing, model evaluation), transfert to forest managers (particularly french ONF) and educational purposes. |
It may help for decision making in forest management in some particular cases. | It may help for decision making in forest management in some particular cases. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 27: | ||
=== System origin === | === System origin === | ||
| − | * The first version was developped by Philippe Dreyfus between | + | * The first version was developped by Philippe Dreyfus (INRA URFM, Avignon, France) between 1994 and 1999. |
| − | * Since 1999 the platform | + | * Since 1999 the platform has been developed by [[François de Coligny]] (INRA AMAP, Montpellier, France), joined by [[Samuel Dufour]] in 2008. |
=== Support for specific issues === | === Support for specific issues === | ||
The supported issues depend on the model which has been integrated in Capsis. It can be for instance | The supported issues depend on the model which has been integrated in Capsis. It can be for instance | ||
| − | growth and biomass estimation, carbon storage, logging, regeneration and mortality estimation, risk management, economical balances, evaluation of different | + | growth and biomass estimation, carbon storage, logging, regeneration and mortality estimation, risk management, economical balances, evaluation of different silvicultural strategies and harvesting scenarii... |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Data and data models == | == Data and data models == | ||
| Line 56: | Line 47: | ||
* simulated data calcultated by specific algorithms | * simulated data calcultated by specific algorithms | ||
| + | Each model can have its own and specific input file formats. | ||
=== Type of information input from user (via GUI) === | === Type of information input from user (via GUI) === | ||
Each model integrated in capsis has its own GUI. This gui allow to set the model input parameters. | Each model integrated in capsis has its own GUI. This gui allow to set the model input parameters. | ||
| − | These parameters | + | These parameters depend on the model. There are various types of inputs : |
* Initial parameters | * Initial parameters | ||
* Evolution parameters | * Evolution parameters | ||
| − | * Intervention parameters | + | * Intervention parameters (managed with plugins that may be compatible with several growth models) |
== Models == | == Models == | ||
| Line 70: | Line 62: | ||
=== Forest models === | === Forest models === | ||
| − | There are | + | There are around 50 models integrated in Capsis : see [http://capsis.cirad.fr/capsis/models capsis models]. |
* stand models | * stand models | ||
| Line 76: | Line 68: | ||
* distance independant tree models | * distance independant tree models | ||
* distance dependant tree models | * distance dependant tree models | ||
| + | * mixt models... | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Decision Support == | == Decision Support == | ||
| Line 86: | Line 76: | ||
=== Definition of management interventions === | === Definition of management interventions === | ||
| − | Capsis supports | + | Capsis supports numerous types of generic interventions: |
| − | + | ||
| − | Each model can also implements specific intervention mechanisms. | + | * thresholds on tree age, height, diameter |
| + | * thinning diagram (cut in girth / diameter classes) | ||
| + | * individual thinning | ||
| + | * thinning with the mouse on a map | ||
| + | * specific strategies like French ONF thinning... | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each model can also implements its specific intervention mechanisms depending on specific parameters. | ||
=== Typical temporal scale of application === | === Typical temporal scale of application === | ||
| − | The temporal scale depends | + | The temporal scale depends on the model: it can be short or long term simulation. The time is discretized in steps. The time step also depends on the model implementation. |
| + | |||
| + | The typical time step is one year but other possible time steps are: day, fortnight (2 weeks), month, 3 years. Some models may manage several years for several processes. | ||
=== Types of decisions supported === | === Types of decisions supported === | ||
| Line 101: | Line 98: | ||
=== Decision-making processes and models === | === Decision-making processes and models === | ||
| − | Capsis integrates optimization | + | The main goals of the models in Capsis are to study various management scenarios to predict plantations growth / forests dynamics to assess production or viability issues. |
| + | |||
| + | Capsis can also host models for very different studies: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * wind risk | ||
| + | * trees / crops interaction (agroforestry) | ||
| + | * tree canopy plasticity | ||
| + | * evolution of biomass in many compartments | ||
| + | * forest fires prevention | ||
| + | * heterogeneous forests study... | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capsis can help elaborate scenarios to reach specific management objectives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Capsis integrates optimization methods to help evaluate various management strategies. It can also be used to run sensitivity analyses on the model parameters. | ||
== Output == | == Output == | ||
| Line 107: | Line 117: | ||
=== Types of outputs === | === Types of outputs === | ||
| − | * stand level table and graphical outputs showing the temporal changes | + | * stand level table and graphical outputs showing the temporal changes |
* stand level 2D viewer | * stand level 2D viewer | ||
* stand level 3D viewer | * stand level 3D viewer | ||
| + | * many file exports with specific formats (plugins with new formats can be added when needed) to connect with data analysis tools or other downstream simulators | ||
=== Spatial analysis capabilities === | === Spatial analysis capabilities === | ||
| − | + | Facilitates links to Geographical Information Systems with [http://www.geotools.org geotools java library] | |
| − | + | ||
=== Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues === | === Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues === | ||
| − | Capsis models can be coupled to other | + | Capsis models can be coupled to other models or frameworks to address interdisciplinary issues. |
| − | Capsis | + | Capsis can also be used as an external model or library. |
| − | For instance | + | For instance, a Capsis-hosted model can be used in the OpenAlea <ref>[http://openalea.gforge.inria.fr]</ref> framework. |
| − | Some | + | Some Capsis models also link to agronomical models (STICS), architectural models (AMAPsim), biomechanical models (FOREOLE) or radiative balance (ARCHIMED, SLIM)... |
== System == | == System == | ||
| Line 135: | Line 145: | ||
=== Usage === | === Usage === | ||
| − | Research level use | + | Research level use / knowledge transfert to expert level users |
=== Computational limitations === | === Computational limitations === | ||
| Line 145: | Line 155: | ||
Capsis provides : | Capsis provides : | ||
* an interactive graphical user interface | * an interactive graphical user interface | ||
| − | * a script mode (without gui) based on groovy | + | * a script mode (without gui) based on java or groovy |
=== Documentation and support === | === Documentation and support === | ||
| − | See Capsis web site <ref>[http://www.inra.fr/capsis capsis web site]</ref> : [http://www.inra.fr/capsis capsis web site] | + | See the Capsis web site <ref>[http://www.inra.fr/capsis capsis web site]</ref> : [http://www.inra.fr/capsis capsis web site] |
=== Installation === | === Installation === | ||
| − | + | A free and open source version is available on the web, it contains only few free models for evaluation: http://capsis.cirad.fr/capsis/download | |
| − | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:48, 14 October 2012
Contents
General System description
System name: Capsis - Computer Aided Projection of Strategies In Silviculture
Acronym: Capsis
Brief overview
Capsis is a software platform which purpose is to host forestry growth and yield / dynamics models. It can help run various silvicultural scenarios by combining a given growth model with silvicultural treatments. It was built by french researchers (INRA, France) for forest research (hypotheses testing, model evaluation), transfert to forest managers (particularly french ONF) and educational purposes.
It may help for decision making in forest management in some particular cases.
Scope of the system
Capsis is a simulation platform for forestry growth / dynamics models. It is a tool for forestry researchers, forest managers and educational purposes. It makes possible to implement models of various types (stand models, distance-independent or distance-dependent tree models, mixt models…), to run simulations and then compare the different scenarios in the same tool.
Thanks to its flexible architecture, it is possible to integrate heterogeneous models (uneven-aged, several species) with various processes (growth, competition, mortality, regeneration…) and to run simulations in interactive or script modes. Some models can have very particular properties, e.g. radiative balance, genetics information at the individual level, internal biomechanics or wood quality.
System origin
- The first version was developped by Philippe Dreyfus (INRA URFM, Avignon, France) between 1994 and 1999.
- Since 1999 the platform has been developed by François de Coligny (INRA AMAP, Montpellier, France), joined by Samuel Dufour in 2008.
Support for specific issues
The supported issues depend on the model which has been integrated in Capsis. It can be for instance growth and biomass estimation, carbon storage, logging, regeneration and mortality estimation, risk management, economical balances, evaluation of different silvicultural strategies and harvesting scenarii...
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
The normal spatial application level of Capsis is the stand level but can be extended to the forest level for specific models.
Forest data input
Capsis input information are
- inventory data that can be imported from files
- simulated data calcultated by specific algorithms
Each model can have its own and specific input file formats.
Type of information input from user (via GUI)
Each model integrated in capsis has its own GUI. This gui allow to set the model input parameters. These parameters depend on the model. There are various types of inputs :
- Initial parameters
- Evolution parameters
- Intervention parameters (managed with plugins that may be compatible with several growth models)
Models
Forest models
There are around 50 models integrated in Capsis : see capsis models.
- stand models
- diameter class models
- distance independant tree models
- distance dependant tree models
- mixt models...
Decision Support
Definition of management interventions
Capsis supports numerous types of generic interventions:
- thresholds on tree age, height, diameter
- thinning diagram (cut in girth / diameter classes)
- individual thinning
- thinning with the mouse on a map
- specific strategies like French ONF thinning...
Each model can also implements its specific intervention mechanisms depending on specific parameters.
Typical temporal scale of application
The temporal scale depends on the model: it can be short or long term simulation. The time is discretized in steps. The time step also depends on the model implementation.
The typical time step is one year but other possible time steps are: day, fortnight (2 weeks), month, 3 years. Some models may manage several years for several processes.
Types of decisions supported
It depends of the integrated model.
Decision-making processes and models
The main goals of the models in Capsis are to study various management scenarios to predict plantations growth / forests dynamics to assess production or viability issues.
Capsis can also host models for very different studies:
- wind risk
- trees / crops interaction (agroforestry)
- tree canopy plasticity
- evolution of biomass in many compartments
- forest fires prevention
- heterogeneous forests study...
Capsis can help elaborate scenarios to reach specific management objectives.
Capsis integrates optimization methods to help evaluate various management strategies. It can also be used to run sensitivity analyses on the model parameters.
Output
Types of outputs
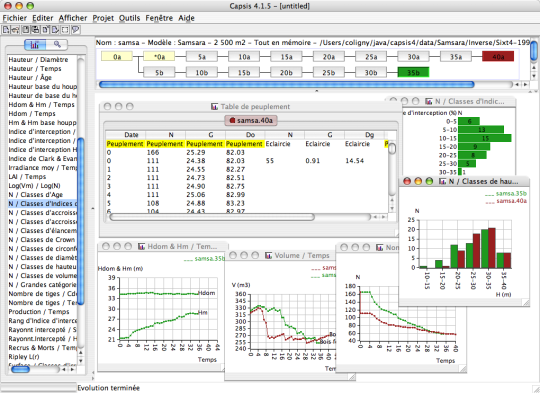
- stand level table and graphical outputs showing the temporal changes
- stand level 2D viewer
- stand level 3D viewer
- many file exports with specific formats (plugins with new formats can be added when needed) to connect with data analysis tools or other downstream simulators
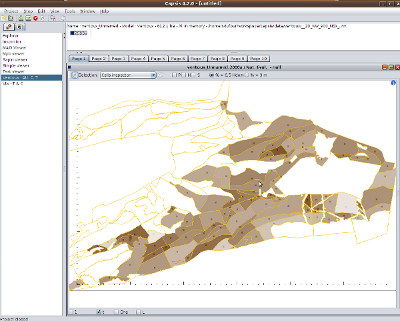
Spatial analysis capabilities
Facilitates links to Geographical Information Systems with geotools java library
Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues
Capsis models can be coupled to other models or frameworks to address interdisciplinary issues. Capsis can also be used as an external model or library. For instance, a Capsis-hosted model can be used in the OpenAlea [1] framework. Some Capsis models also link to agronomical models (STICS), architectural models (AMAPsim), biomechanical models (FOREOLE) or radiative balance (ARCHIMED, SLIM)...
System
System requirements
- Operating Systems: Linux / Windows / Mac Os X
- Other software needed : Java 1.6
Architecture and major DSS components
Desktop application
Usage
Research level use / knowledge transfert to expert level users
Computational limitations
System memory limitation
User interface
Capsis provides :
- an interactive graphical user interface
- a script mode (without gui) based on java or groovy
Documentation and support
See the Capsis web site [2] : capsis web site
Installation
A free and open source version is available on the web, it contains only few free models for evaluation: http://capsis.cirad.fr/capsis/download
References
Cited references
External resources
- de Coligny F., 2007. Efficient Building of Forestry Modelling Software with the Capsis Methodology. In: Fourcaud T, Zhang XP, eds. Plant Growth Modeling and Applications. Proceedings of PMA06. Los Alamitos, California: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 216-222.