Difference between revisions of "EMIS"
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
== Decision Support == | == Decision Support == | ||
| − | + | ||
=== Definition of management interventions === | === Definition of management interventions === | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
Prescription enumerating all selected possibilities at stand level, coarser information in GIS layers. | Prescription enumerating all selected possibilities at stand level, coarser information in GIS layers. | ||
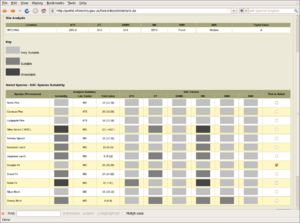
| + | [[Image:EMIS_restocking_advices.png|thumb|300px|EMIS screenshot showing some restocking advices for the selected site and species]] | ||
=== Typical temporal scale of application === | === Typical temporal scale of application === | ||
Revision as of 20:55, 30 November 2009
General System description
System name: Establishment Management Information System
Acronym: EMIS
Brief overview
The aim of EMIS was integrate knowledge of site and plant characteristics to provide a whole lifecycle view of scenario options. Fundamentally based on ESC, EMIS extends site selection capabilities by integrating wind hazard, timber quality and other models to provide a broader picture of the establishment opportunities on conifer restock sites.
Contents
Scope of the system
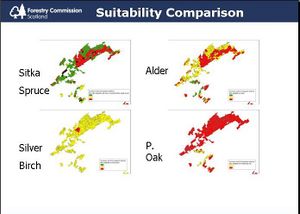
The Establishment Management Information System (EMIS) is a decision support tool that integrates existing advice on tree establishment for upland restocking on a site specific basis. Site information inputted by the user allows calculation of environmental variables that constrain species choice and identifies appropriate on-site management practices. EMIS currently provides advice encompassing the main commercial upland conifer species, plus birch. Whilst all potential system inputs and interactions have been investigated, primary drivers were identified to ensure that the system evolves, guided by operational requirements and existing knowledge. This is a web-based DSS integrated with the other components of the GB Forestry DSS.
System origin
- Developed by Mike Perks, Alan Harrison and Stephen Bathgate. Being an integration product its development would not have been possible without fundamental building blocks such as ESC, ForestGALES and many other Forest Research models.
- Currently free to use at stand scale via web.
- Some small scale use in public and private sector.
Support for specific issues
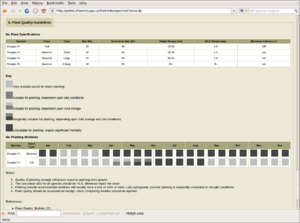
Afforestation: site classification, forest vegetation managements, species selection, wind hazard, timber quality, forest transformation, fertilisation, and plant quality guidelines.
Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type
- Silvicultural
- Certification
- Conservation
- Restoration
- Development choices / land use zoning
- Policy/intervention alternatives
- Sustainability impact assessment (SIA)
Capability to support decision making phases
- Intelligence:
- gives user detailed site analysis - climate and soil parameters
- Design:
- provides site analysis in context of many themes
- Choice:
- allows user to vary species choice, management options
- Monitor:
- highlights risks which in theory could encourage monitoring
Related systems
- GB Forestry DSS
- Conifer Timber Quality Model
- ESC
- ForestGALES
- Herbicide advisor
- Hylobius Management Support System
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
Web based tool operates at stand scale, ca 1-5 hectares, batch GIS tool has generated regional and national scenarios.
Forest data input
Location via OS GB six figure grid reference, eg NT090950. User also supplies an FC soil type (eg 1g, 4, 7bz), lithology/geology, the presence of heather, aspect and slope.
Type of information input from user (via GUI)
User selects one or more tree species for detailed analysis from an intermediate screen.
Models
Forest models
Growth, wind hazard (ForestGALES), timber quality (CTQM), planting windows, fertiliser, species suitability (ESC), cultivation, risk and brash/stump models.
Decision Support
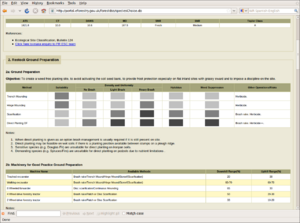
Definition of management interventions
Timing of planting, fertilisation, rotations, species choice.
Prescription enumerating all selected possibilities at stand level, coarser information in GIS layers.
Typical temporal scale of application
Allows full lifecycle analysis of a rotation 30-80+ years.
Output
Types of outputs
Stand version generates tables in HTML, thematic maps can be generated via a batch tool for visualisation in GIS, assuming suitable soil data is available. Reports can be exported as .pdf files.
Spatial analysis capabilities
EMIS will be available as document-wrapped-style web services to allow integration with GIS systems.
System
System requirements
- Java library deployed on Linux and Windows. UI available at stand level via web, or batch system via command line.
- Utilises many open source Java libraries, GRASS GIS or ArcGIS required for batch stage. Data currently managed in Oracle database or as raster files.
- Beta trial
Architecture and major DSS components
3 tier architecture ( UI, Models, Data)
Web based UI using JSP, HTML, CSS
Also desktop batch tool for GIS processing using Java.
Models are implemented in java and EMIS libraries assemble these in order to answer user questions. These can be called independently if necessary.
Highly modular, components based on themes eg species suitability, wind hazard, etc.
Some simple web service interfaces developed using document literal style WSDL/SOAP and REST.
Basic dataflow is location accesses site climate data, this and other user input data are then processed by the various models to generate outputs.
Usage
Used in education, public and private sector forestry and research.
Computational limitations
Typical processing time for Scottish Forest District 6-8 hours (vector-raster intersection step takes 5-6 hours, models execute over 4000 components in about 1 hour, but this varies according to species etc). Large scale spatial intersections sometimes exhaust machine memory with ArcGIS.
User interface
Web UI requires some understanding of soil types, OS grid references, reference to geological maps. Interpretation of information can be challenging so support is being developed.
Documentation and support
None to date. Support available via email.
Installation
- Prerequisite knowledge: Requires web browser. Server installation requires specialised skills and tools. Batch mode requires some configuration on host machine.
References
External resources
- Forest Research Decision Support Portal (note registration required)
- PERKS, M.P., A.J. HARRISON et S.J. BATHGATE (2007): Establishment Management Information System (EMIS): Delivering Good Practice Advice on Tree Establishment in the Uplands of Britain. In REYNOLDS, K., M. MOHL et M. SHANNON (Eds.): Sustainable forestry: from monitoring and modelling to knowledge management. CABI Publishing, pp 412-424.
- Decision support system
- GB Forestry DSS
- British DSS
- Afforestation management
- Ecological classification
- Fertilization
- Forest transformation
- Forest vegetation management
- Plant quality
- Species selection
- Wind hazard
- Wood quality
- Yield prediction
- Pinus sylvestris
- Pinus nigra subsp. salzmannii var. corsicana
- Pinus contorta
- Larix decidua
- Larix kaempferi
- Pseudotsuga menziesii
- Abies procera
- Abies grandis
- Picea sitchensis
- Picea abies
- Betula spp.
- Stand level
- Operational planning
- Multi-platform application
- Web application