Difference between revisions of "Knowledge Management tools"
From COST Action FP0804: FORSYS
m (→Knowledge Management tools for forest management DSS's) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Gray's classification <ref> Peter H. Gray, A problem-solving perspective on knowledge management practices, Decision Support Systems, Volume 31, Issue 1, May 2001, Pages 87-102. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9236(00)00121-4 Available here]</ref> | Gray's classification <ref> Peter H. Gray, A problem-solving perspective on knowledge management practices, Decision Support Systems, Volume 31, Issue 1, May 2001, Pages 87-102. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9236(00)00121-4 Available here]</ref> | ||
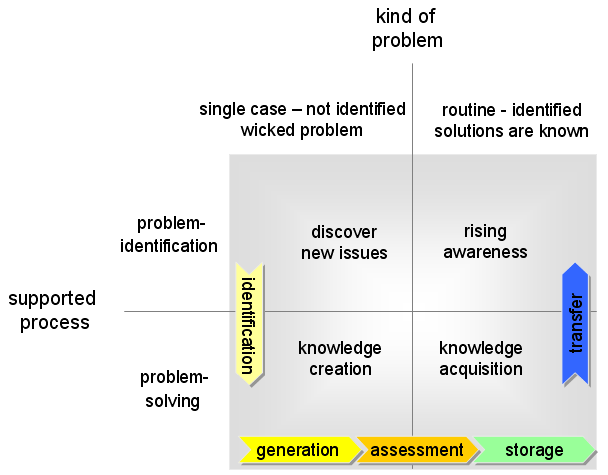
| − | recognizes different types of managing knowledge with regards action motivations in two different types of problems. The motivation can either be ''problem identification'' or ''problem solving'', and the problem can be either ''unique/new'' or ''previously solved''. Combining these in 2*2 matrix shows us four types of KM: (1) ''' | + | recognizes different types of managing knowledge with regards action motivations in two different types of problems. The motivation can either be ''problem identification'' or ''problem solving'', and the problem can be either ''unique/new'' or ''previously solved''. Combining these in 2*2 matrix shows us four types of KM: (1) '''Discovering new issues''', (2) '''Creating knowledge''', (3) '''Acquiring knowledge''', and (4) '''Raising awareness'''. Shifting between these ascendingly can be seen as (a) ''identifying'', (b) ''preserving/storing'', and (c) ''distributing/transferring'' knowledge (see Fig. 1 below). |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gray_redrawn.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Fig. 1.''' Knowledge management types within decision problems after Gray (2003). | ||
Other options to classify... | Other options to classify... | ||
Revision as of 23:03, 22 November 2009
Contents
Knowledge Management tools for forest management DSS's
List of potential KM tools
| Tool | Classification 1 | Classification 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge maps | ||
| Databases | ||
| Expert systems | ||
| Free-content information collaboratories | ||
| Web portals | ||
| Electronic yellow-page directories | ||
| Communities of practice | ||
| Frequently asked questions | ||
| Scientific content management sites | ||
| Online scientific journals | ||
| Library services | ||
| Best practices and lessons learned | ||
| Lectures and story telling | ||
| Apprenticeship programs | ||
| Web-based learning | ||
| Simulation models |
Options to classify the tools
Gray's classification [1] recognizes different types of managing knowledge with regards action motivations in two different types of problems. The motivation can either be problem identification or problem solving, and the problem can be either unique/new or previously solved. Combining these in 2*2 matrix shows us four types of KM: (1) Discovering new issues, (2) Creating knowledge, (3) Acquiring knowledge, and (4) Raising awareness. Shifting between these ascendingly can be seen as (a) identifying, (b) preserving/storing, and (c) distributing/transferring knowledge (see Fig. 1 below).
Fig. 1. Knowledge management types within decision problems after Gray (2003).
Other options to classify...
References
- ↑ Peter H. Gray, A problem-solving perspective on knowledge management practices, Decision Support Systems, Volume 31, Issue 1, May 2001, Pages 87-102. Available here