Difference between revisions of "MONTE"
A trasobares (Talk | contribs) (→System origin) |
A trasobares (Talk | contribs) (→System origin) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== System origin === | === System origin === | ||
* Developed by Timo Pukkala, Antoni Trasobares and Marc Palahí. | * Developed by Timo Pukkala, Antoni Trasobares and Marc Palahí. | ||
| − | * MONTE has been applied to several regions in Spain such as Catalonia, Castilla-León and Aragón. If reliable data (digital terrain model, digital maps, forest inventory, etc.) and models (growth and yield models, volume functions, etc.) are available | + | * MONTE has been applied to several regions in Spain such as Catalonia, Castilla-León and Aragón. If reliable data (digital terrain model, digital maps, forest inventory, etc.) and models (growth and yield models, volume functions, etc.) are available the system can be applied to any other region in Spain or in another country. |
=== Support for specific issues === | === Support for specific issues === | ||
Revision as of 19:55, 1 June 2010
General System description
System name: MONTE
Brief overview
MONTE is a forest management planning software that allows both evaluating the current estate of a forest and preparing specific management plans for a stated temporal goal.
Contents
System origin
- Developed by Timo Pukkala, Antoni Trasobares and Marc Palahí.
- MONTE has been applied to several regions in Spain such as Catalonia, Castilla-León and Aragón. If reliable data (digital terrain model, digital maps, forest inventory, etc.) and models (growth and yield models, volume functions, etc.) are available the system can be applied to any other region in Spain or in another country.
Support for specific issues
Harvest scheduling, timber production, yield prediction, non-wood forest productions, recreation facilities, biodiversity conservation, and landscape quality.
Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type
- Silvicultural
- Certification
- Conservation
- Development choices / land use zoning
- Policy/intervention alternatives
Capability to support decision making phases
- Intelligence:
- The current conditions of the forest can be analysed and the management goals established.
- Design:
- The simulation tool run the different management possibilities among the restrictions imposed by the input data.
- Choice:
- Heuristic tools are used in order to ensure the best management option is the chosen one by the manager.
- Monitor:
- No implemented.
Related systems
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
The normal spatial application level of MONTE is the forest level, holding various stands.
Forest data input
MONTE input information are inventory data that can be imported from files with .xls or .mdb extensions.
The input data required depends on the characteristics of the stand. Thus, for each diameter class the species, diameter and number of stems is needed, and then, site index, age and dominant height for even-aged stands, and altitude, continentality, and five-last-years growth for uneven-aged stands have to be inputted.
In order to allow the 3D results visualization some geographic files must be provided: a digital elevation model (DEM) where stands have to be defined, each silviculture treatment alternative, and the optimization module result.
Type of information input from user (via GUI)
Forest management goals have to be selected within the ones showed in the user interface. More than one goal may be selected, in order to adress forest multi-objective management. The showed goals are both yield and economic goals and conservationist and leisure goals. Once selected, goals must be weighted according to the user preferences, in order to proceed towards the optimization module.
Models
Forest models
Models implemented in MONTE simulate silvicultural treatment schedules according to the stand variables previously given.
Currently MONTE has implemented models for the management of either even-aged, uneven-aged, pures or mixed forest stands of the following species: Pinus uncinata, Pinus sylvestris, Pinus nigra, Pinus halepensis, Pinus pinea, Abies alba, and some hardwoods.
Social models
Recreation can be selected among the management goals.
Decision Support
Definition of management interventions
Manager is advised on which silvicultural treatments, how, and when (time of harvest, regeneration methods, thinnings, etc.) should be done in order to achieve the previously chosen management goals.Typical temporal scale of application
Tactical planning.
Types of decisions supported
- Management level
- strategic decisions
- operating control decisions
- Management function
Decision-making processes and models
Output
Types of outputs
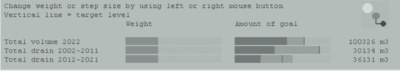
The heuristically generated solution is displayed as a bar chart where reached and goal values are shown.
For each management stand, the future development can be displayed with a static visualization tool, together with some recommendations about the treatments that should be done within a short time period in order to achieve the proposed goals.
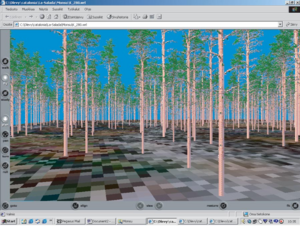
A 3D visualization tool enables landscape analyses of the selected management schedules. Also, the creation of VRML (Virtual Reality Modelling Language) files for each stand is allowed, enabling the visualization of the stand results in other software with this capability (common web-browsers, etc.).
Spatial analysis capabilities
Visualization tools are implemented within the MONTE framework, driving to spatial development and landscape analyses.
References
External resources
- foreco technologies website
- PALAHÍ, M., T. PUKKALA et A. TRASOBARES (2004): Presentación del sistema de planificación forestal MONTE. Revista Montes 4º Trimestre 2004, Nº 78 (In Spanish).
- Decision support system
- Spanish DSS
- Harvest scheduling model
- Yield prediction
- Conservation system
- Economic evaluation
- Non-wood forest production
- Landscape quality
- Multipurpose DSS
- Socio-economic model
- Pinus uncinata
- Pinus sylvestris
- Pinus nigra
- Pinus halepensis
- Pinus pinea
- Abies alba
- Forest level
- Tactical planning
- Goal-driven DSS
- Genetic algorithms
- Tabu search
- Simulated annealing
- Random ascent
- HERO
- 3D visualization