Difference between revisions of "FFIREDESSYS"
Ola Eriksson (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
FFIREDESSYS is a [[decision support system]] that estimates the structural forest fire risk on a global scale, introducing the use of fuzzy sets and fuzzy algebra concepts. | FFIREDESSYS is a [[decision support system]] that estimates the structural forest fire risk on a global scale, introducing the use of fuzzy sets and fuzzy algebra concepts. | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Decision support system]] | [[Category:Decision support system]] | ||
[[Category:Greek DSS]] | [[Category:Greek DSS]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 66: | Line 59: | ||
=== Definition of management interventions === | === Definition of management interventions === | ||
| − | Knowing an estimated forest fire risk enables local authorities to prevent forest fire occurrence with | + | Knowing an estimated forest fire risk enables local authorities to prevent forest fire occurrence with silvicultural interventions and to increase the forest fight means in the foreseen risky areas. |
=== Typical temporal scale of application === | === Typical temporal scale of application === | ||
New forest fire risk estimation must be made each year. | New forest fire risk estimation must be made each year. | ||
| + | <div style="color:red"> | ||
=== Types of decisions supported === | === Types of decisions supported === | ||
*Management level | *Management level | ||
| Line 100: | Line 94: | ||
=== Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues === | === Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues === | ||
| − | Evaluate interactions between different basic information types (biophysical, economic, social). Produce coordinated results for decision makers operating at different spatial scales facilitate social negotiation and learning | + | Evaluate interactions between different basic information types (biophysical, economic, social). Produce coordinated results for decision makers operating at different spatial scales facilitate social negotiation and learning </div> |
| + | |||
== System == | == System == | ||
=== System requirements === | === System requirements === | ||
| − | * Operating Systems: The DSS runs on any type of Pentium PC that uses Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows NT. The system is not portable only to Unix machines. | + | * Operating Systems: The DSS runs on any type of Pentium PC that uses Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows NT. The system is not portable only to Unix machines. |
| − | + | ||
* Development status: an initial version was developed (2004) | * Development status: an initial version was developed (2004) | ||
| Line 120: | Line 114: | ||
=== User interface === | === User interface === | ||
It has a friendly user interface that uses menus, screens and pop-up menus. The choices are done by the use of keyboard buttons. | It has a friendly user interface that uses menus, screens and pop-up menus. The choices are done by the use of keyboard buttons. | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
===External resources=== | ===External resources=== | ||
| − | ILIADIS L.S. (2005): A decision support system applying an integrated fuzzy model for long-term forest fire risk estimation. ''Environmental Modelling & Software'', 20, 613-621. | + | * ILIADIS L.S. (2005): A decision support system applying an integrated fuzzy model for long-term forest fire risk estimation. ''Environmental Modelling & Software'', 20, 613-621. |
Latest revision as of 07:58, 14 October 2012
General System description
System name:
Acronym: FFIREDESSYS
Brief overview
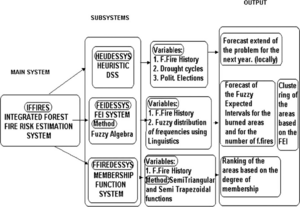
FFIREDESSYS is a decision support system that estimates the structural forest fire risk on a global scale, introducing the use of fuzzy sets and fuzzy algebra concepts.
Contents
Scope of the system
The purpose of the FFIREDESSYS is to be used as a pilot system and to lead the way for further fuzzy systems development in the near future. This is the first DSS which use fuzzy algebra in this domain and from this point of view the FFIREDESSYS is globally unique.
System origin
- Developed by L.S. Iliadis in 2003.
- how was it developed
- is it a commercial product
- does it have real-life application cases
Support for specific issues
Forest fire risk estimation
Capability to support decision making phases
(NOTE I do not quite know what to do with this, as I do not understand it myself, although it seems related to system use)
(Click here to see a more detailed explanation)
- Intelligence (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Design (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Choice (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Monitor (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
Related systems
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
Global level (e.g., a validation test has been made in the whole Greece estimating forest fire risk for each prefecture).
Forest data input
There is a Knowledge Base containing forest fire data.
Models
Forest models
A fuzzy system model for forest fire risk estimation was used, applying both trapezoidal and triangular membership functions.
Decision Support
Definition of management interventions
Knowing an estimated forest fire risk enables local authorities to prevent forest fire occurrence with silvicultural interventions and to increase the forest fight means in the foreseen risky areas.
Typical temporal scale of application
New forest fire risk estimation must be made each year.
Types of decisions supported
- Management level
- strategic decisions
- administrative decisions
- operating control decisions
- Management function
- planning decisions
- organizing decisions
- command decisions
- control decisions
- coordination decisions
- decision making situation
- unilateral
Output
Types of outputs
Types of outputs produced (tables, maps, 3-D visualizations, pre-programmed summaries, etc)
Spatial analysis capabilities
- integrated capabilities
- facilitates links to GIS (wizards, etc.)
- provides standard data import/export formats
- allows spatial analysis (e.g. topology overlays (e.g. multi layering of different maps, selection of objects based on selection criteria, aggregation by attributes (e.g. areas of similar characteristics), Linking by logical means, Statistics by area, analysis with digital terrain model)
Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues
Evaluate interactions between different basic information types (biophysical, economic, social). Produce coordinated results for decision makers operating at different spatial scales facilitate social negotiation and learning
System
System requirements
- Operating Systems: The DSS runs on any type of Pentium PC that uses Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows NT. The system is not portable only to Unix machines.
- Development status: an initial version was developed (2004)
Architecture and major DSS components
Developed using MS Visual Basic. It is an auto run system that has been developed in the laboratory of Forest Informatics of Democritus University of Thrace, Greece.
Usage
Government and research use.
Computational limitations
It has proved to run properly in a Pentium III or above.
User interface
It has a friendly user interface that uses menus, screens and pop-up menus. The choices are done by the use of keyboard buttons.
References
External resources
- ILIADIS L.S. (2005): A decision support system applying an integrated fuzzy model for long-term forest fire risk estimation. Environmental Modelling & Software, 20, 613-621.