Difference between revisions of "LEaRNForME"
m (1 revision: Import from testwiki) |
|||
| (57 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{DSS, Wiki quality control | |
| − | + | |Has flag=N/A | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | {{DSS, Name, responsible organisation and contact person | |
| − | + | |Has full name=Landslide Erosion and Runoff: Neural Forest Estimation ModEls | |
| − | + | |Has acronym=LEaRNForME | |
| − | + | |Has wiki contact person=Gianfranco Scrinzi | |
| − | + | |Has wiki contact e-mail=gianfranco.scrinzi@entecra.it | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | {{DSS, Software identification | |
| − | + | |Has software=LEaRNForME.Software | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | {{DSS, Description | |
| − | + | |Has description=LEaRNForME is an instrument for the land planning able to recognise the role of the vegetation cover in controlling some hydro geological instability phenomena. This evaluation will give the opportunity to introduce environmental issues into forest planning. | |
| − | + | |Has modelling scope=Forest indicators | |
| − | = | + | |Has temporal scale=Long term (strategic), Short term (operational) |
| − | + | |Has spatial context=Spatial with no neighbourhood interrelations | |
| − | + | |Has spatial scale=Forest level, Stand level | |
| − | + | |Has objectives dimension=Multiple objectives | |
| − | + | |Has goods and services dimension=Market wood products, Non-market services | |
| − | + | |Has decision making dimension=Single decision maker | |
| − | + | |Has forest management goal=multi-functional | |
| − | = | + | |Supports tree species=all the Italian forest types |
| − | + | |Supports silvicultural regime=user defined | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | === Scope of the system == | + | {{DSS, Concrete application |
| + | |Has typical use case=one forest stand managed at a time | ||
| + | |Has country=Italy | ||
| + | |Has number of users=<=10 | ||
| + | |Has number of real-life applications=<=10 | ||
| + | |Has utilisation in education=presentation/demo | ||
| + | |Has tool dissemination=scientific and technical publications, web site, conferences | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{DSS, Decision support techniques used in the DSS | ||
| + | |Has decision support techniques=LEaRNForME.Decision support techniques | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{DSS, Support of Knowledge Management | ||
| + | |Has knowledge management processes=LEaRNForME.Knowledge management process | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{DSS, Support of social participation | ||
| + | |Has support for social participation=LEaRNForME.Support of social participation | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{DSS, DSS development | ||
| + | |Has DSS development=LEaRNForME.Description of DSS development | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{DSS, Documentation | ||
| + | |Has website=http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm | ||
| + | |Has online demo=http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm | ||
| + | |Has manual=Yes | ||
| + | |Has technical documentation=Yes | ||
| + | |Has reference=Andrenelli et al., 2007; Scrinzi et al., 2006; Gregori et al., 2007; Scrinzi et al., 2005 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | = ADDITIONAL INFORMATION (needs to be migrated using the "edit with form" link) = | ||
| + | == Scope of the system == | ||
| + | [[Image: Schema_approccio_eng.gif|thumb|400px|The schema of LEaRNForME]] | ||
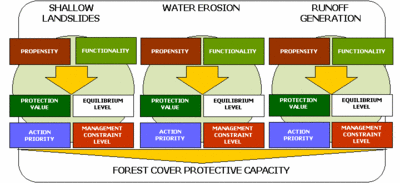
A procedure has been conceived and implemented in order to support the forester in classifying each homogeneous land unit for: | A procedure has been conceived and implemented in order to support the forester in classifying each homogeneous land unit for: | ||
* predisposition to instability phenomena (termed "propensity") such as shallow landslides, water erosion and runoff generation; | * predisposition to instability phenomena (termed "propensity") such as shallow landslides, water erosion and runoff generation; | ||
* vegetation cover functionality in contrasting these events. | * vegetation cover functionality in contrasting these events. | ||
| + | |||
Both aspects have to be described and modelled by means of distinctive sets of variables; neural network analysis is then applied to a comprehensive set of study cases. The resulting evaluations of predisposition and functionality are combined into four different indexes with descriptive and planning significance: | Both aspects have to be described and modelled by means of distinctive sets of variables; neural network analysis is then applied to a comprehensive set of study cases. The resulting evaluations of predisposition and functionality are combined into four different indexes with descriptive and planning significance: | ||
* equilibrium level, a rough estimation of the balance between tendency and cover protection; | * equilibrium level, a rough estimation of the balance between tendency and cover protection; | ||
| Line 34: | Line 64: | ||
* action priority, preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices. | * action priority, preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices. | ||
At present only the models devoted to the protection from shallow landslides and soil water erosion are operating; analogous procedure for runoff generation is in progress. | At present only the models devoted to the protection from shallow landslides and soil water erosion are operating; analogous procedure for runoff generation is in progress. | ||
| + | To try the online-models go to this Web page: http://www.isafa.it/scientifica/assestamento/riselvitalia43/modelli_eng.htm/. | ||
| − | + | == System origin == | |
| − | + | LEaRNForME was developed during 2001-2007 by Gianfranco Scrinzi, David Galvagni and Giacomo Colle in the Forest Monitoring and Management Unit (Unità di ricerca per il Monitoraggio e la Pianificazione forestale) (http://mpf.entecra.it/) of Italian Council for Research in Agriculture (Consiglio per la Ricerca e la Sperimentazione in Agricoltura) (http://sito.entecra.it). | |
| − | + | == Support for specific issues == | |
| − | + | LEaRNForME assists the forestry on site where shallow landslide, water erosion and runoff generation are instability phenomena. | |
| − | + | == Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type == | |
| − | * Forest planning | + | * Forest planning. |
| − | * Territorial planning | + | * Territorial planning. |
| − | * Protection | + | * Protection. |
| − | * Prevention | + | * Prevention. |
| − | + | == Capability to support decision making phases == | |
* Intelligence: the system use a fully automatic, congruent, progressive and recordable procedure. | * Intelligence: the system use a fully automatic, congruent, progressive and recordable procedure. | ||
* Design: forest planner input data to evaluate propensity and protective functionality of forest. | * Design: forest planner input data to evaluate propensity and protective functionality of forest. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 84: | ||
* Monitor: implemented for test areas. | * Monitor: implemented for test areas. | ||
| − | + | == Related systems == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | === Data and data models === |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Typical spatial extent of application == |
| − | The forest data input | + | The typical spatial extent of application is the forest management plan. |
| + | There isn’t a base spatial unit for the output, it’s depend on what extension data input refer. But the minimum reasonable unit is the forest plot. | ||
| + | Definitely we can say that the typical spatial extent of application is the single property scale. | ||
| − | === Type of information input from user (via GUI) | + | == Forest data input == |
| + | The forest data input are about vegetation cover and forest management disturbances. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Type of information input from user (via GUI) == | ||
The user provides basic input data about the site conditions (lithology, aspect, slope, vegetation cover, erodibility, land use, practices, disturbances, etc.). | The user provides basic input data about the site conditions (lithology, aspect, slope, vegetation cover, erodibility, land use, practices, disturbances, etc.). | ||
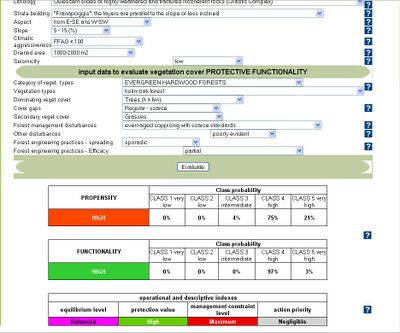
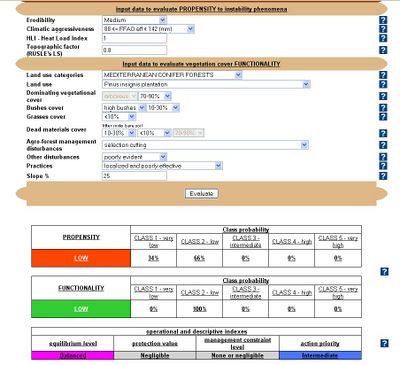
In the shallow landslides model, the users input data to evaluate propensity to instability phenomena concerning: lithology, strata bedding, aspect, slope, climatic aggressiveness, drained area and seismicity. To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data about category of vegetation types, vegetation types, dominating vegetation cover, cover gaps, secondary vegetation cover, forest management disturbances, other disturbances, forest engineering practices, forest engineering practices. | In the shallow landslides model, the users input data to evaluate propensity to instability phenomena concerning: lithology, strata bedding, aspect, slope, climatic aggressiveness, drained area and seismicity. To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data about category of vegetation types, vegetation types, dominating vegetation cover, cover gaps, secondary vegetation cover, forest management disturbances, other disturbances, forest engineering practices, forest engineering practices. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 103: | ||
To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data concerning land use categories, land use, dominating vegetational cover, bushes cover, grasses cover, dead materials cover, agro-forest management disturbances, practices, slope. | To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data concerning land use categories, land use, dominating vegetational cover, bushes cover, grasses cover, dead materials cover, agro-forest management disturbances, practices, slope. | ||
| − | == Models == | + | |
| + | === Models === | ||
The system use Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models. | The system use Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models. | ||
| − | + | == Forest models == | |
| − | + | == Social models == | |
| − | == Decision Support == | + | === Decision Support === |
| − | + | == Definition of management interventions == | |
| + | [[Image: Shallow_landslides.jpeg|thumb|400px|The shallow landslides form]] | ||
| + | [[Image: Soil_water_erosion.jpeg|thumb|400px|The soil water erosion form]] | ||
The intersection of the vegetation functionality and land propensity to an instability phenomenon through complex mathematical functions gives four useful indices for soil conservation purposes. | The intersection of the vegetation functionality and land propensity to an instability phenomenon through complex mathematical functions gives four useful indices for soil conservation purposes. | ||
The user has to interpret this following indices. | The user has to interpret this following indices. | ||
| Line 89: | Line 122: | ||
* protection value: it assesses the ability of the vegetation in controlling land degradation. The protection value is classified into three classes (“high”, “fair” and “negligible”) according to a set of sigmoid functions; | * protection value: it assesses the ability of the vegetation in controlling land degradation. The protection value is classified into three classes (“high”, “fair” and “negligible”) according to a set of sigmoid functions; | ||
* constraint level: this index expresses the degree of limitation with respect to timber-oriented management in relation to the assessed protection value. The classes of constraint are three: “none or negligible”, allowing the adoption of even very intensive cultural systems; “intermediate”, in which only cutting and harvesting techniques that assure the integrity of root apparatus and soil should be allowed; “maximum”, where only cares devoted to the enhancement of the protective functionality of the vegetation cover should be permitted (woodlands destined primarily to the environmental protection); | * constraint level: this index expresses the degree of limitation with respect to timber-oriented management in relation to the assessed protection value. The classes of constraint are three: “none or negligible”, allowing the adoption of even very intensive cultural systems; “intermediate”, in which only cutting and harvesting techniques that assure the integrity of root apparatus and soil should be allowed; “maximum”, where only cares devoted to the enhancement of the protective functionality of the vegetation cover should be permitted (woodlands destined primarily to the environmental protection); | ||
| − | * action priority: this index assumes some planning importance by representing a preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices both for increasing the vegetation cover and for runoff control. The conceptual approach is addressed to prevent the degradation phenomena rather then to reclaim compromised situations. The model provides three classes of “action priority” (“high”, “intermediate” and “negligible”) | + | * action priority: this index assumes some planning importance by representing a preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices both for increasing the vegetation cover and for runoff control. The conceptual approach is addressed to prevent the degradation phenomena rather then to reclaim compromised situations. The model provides three classes of “action priority” (“high”, “intermediate” and “negligible”). |
| − | + | == Typical temporal scale of application == | |
Planning and operational level. | Planning and operational level. | ||
| − | + | == Types of decisions supported == | |
| − | * | + | * Management and sylvicoltural actions. |
| − | * | + | * Strategic decisions. |
| − | * | + | * Operating control decisions. |
| + | |||
| + | == Decision-making processes and models == | ||
| + | |||
| − | === | + | === Output === |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Types of outputs == |
| + | The outputs of LEaRNForME Web system are qualitative indices. | ||
| + | The outputs of LEaRNForME in stand-alone system are maps and table. | ||
| − | == | + | == Spatial analysis capabilities == |
| − | + | LEaRNForME in stand-alone system integrates weighted overlay capabilities using GIS functions. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | == Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues == |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | === System === |
| − | + | ||
| − | == System == | + | == System requirements == |
| + | The Web application runs on multiplatform environment, only an Internet access and a Web browser is required. | ||
| + | The stand-alone application requires ArcView 3.x and MS Access. | ||
| − | == | + | == Architecture and major DSS components == |
| − | + | LEaRNForME is both a stand-alone and a Web application. | |
| − | + | LEaRNForME is a modular system. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Usage == |
| − | + | Forest management and planning, educational. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Computational limitations == |
| − | + | No limitations for the Web application; in the stand-alone GIS application it depends on hardware and software used. | |
| − | == | + | == User interface == |
| − | + | The user has to fill the tables for each instability phenomena: in some case he has to select between the proposed values in the pull down menu. | |
| + | It’s not necessary specific computer knowledge for using the system, but geological and forestry comptences is required to choose the appropriate classes for each variable. | ||
| − | == | + | == Documentation and support == |
| − | + | Information about LEaRNForME can be found at the [http://www.ricercaforestale.it/riselvitalia/?q=node/82 Ri.Selv.Italia project website]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == Installation == |
| − | + | Installation not needed. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | = References = | ||
| − | == | + | == Cited references == |
| − | == | + | == External resources == |
| + | * Andrenelli M.C., Colle G., Galvagni D., Giannetti F., Gregori E., Scrinzi G., Zorn G.– Assessing the protective role of the forest cover against hydrogeological disturbances:a GIS-based tool for forest planning - IUFRO International Conference: "NATURAL HAZARDS AND NATURAL DISTURBANCES IN MOUNTAIN FORESTS" - Trento, ITALY (September 18th-21th, 2007); | ||
| + | * Gregori E., Andrenelli M. C., Zorn G., 2007 – Soil and hillslope management using scenario analysis and runoff-erosion models: a critical evaluation of current techniques. International Conference in Florence, ITALY (7th-9th May 2007); | ||
| + | * Andrenelli M. C., Galvagni D., Gregori E., Scrinzi G., Zorn G. Colle G., , 2006 – Propensione all’erosione idrica del suolo: un approccio valutativo in ambiente gis mediante l’utilizzo di reti neurali. - Convegno Nazionale SISS : "Suolo Ambiente Paesaggio", Imola 27-30 giugno 2006; | ||
| + | * Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G. Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2006 – Un modello di valutazione della funzionalità protettiva del bosco per la pianificazione forestale: la componente stabilità dei versanti rispetto ai fenomeni franosi superficiali. Forest@ 3 (1): 98-155; | ||
| + | * Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G., Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2005 - Boschi e fenomeni franosi superficiali: modello per la valutazione dell'azione protettiva. Estimo e Territorio (Ed agricole - il Sole24ore), anno LXVIII - n.12 - dicembre 2005, pp.30-47; | ||
| + | * Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G. Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2005 – Un modello di valutazione della funzionalità protettiva del bosco per la pianificazione forestale: la componente stabilità dei versanti rispetto ai fenomeni franosi superficiali., 66 p. | ||
| − | + | Every documentation about LEaRNForME and research processes can find in the http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm | |
| − | Every documentation about | + | |
Latest revision as of 16:42, 2 April 2013
Contents
- 1 Wiki quality control
- 2 Name, responsible organisation and contact person
- 3 Software identification
- 4 Description
- 5 Concrete application
- 6 Decision support techniques used in the DSS
- 7 Support of Knowledge Management
- 8 Support of social participation
- 9 DSS development
- 10 Documentation
- 11 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION (needs to be migrated using the "edit with form" link)
- 11.1 Scope of the system
- 11.2 System origin
- 11.3 Support for specific issues
- 11.4 Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type
- 11.5 Capability to support decision making phases
- 11.6 Related systems
- 11.7 Typical spatial extent of application
- 11.8 Forest data input
- 11.9 Type of information input from user (via GUI)
- 11.10 Forest models
- 11.11 Social models
- 11.12 Definition of management interventions
- 11.13 Typical temporal scale of application
- 11.14 Types of decisions supported
- 11.15 Decision-making processes and models
- 11.16 Types of outputs
- 11.17 Spatial analysis capabilities
- 11.18 Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues
- 11.19 System requirements
- 11.20 Architecture and major DSS components
- 11.21 Usage
- 11.22 Computational limitations
- 11.23 User interface
- 11.24 Documentation and support
- 11.25 Installation
- 12 References
Wiki quality control
| Has flag | N/A |
|---|
Name, responsible organisation and contact person
| Has full name | Landslide Erosion and Runoff: Neural Forest Estimation ModEls |
|---|---|
| Has acronym | LEaRNForME |
| Has wiki contact person | Gianfranco Scrinzi |
| Has wiki contact e-mail | gianfranco.scrinzi@entecra.it |
Software identification
| Has software | LEaRNForME.Software |
|---|
Description
| Has description | LEaRNForME is an instrument for the land planning able to recognise the role of the vegetation cover in controlling some hydro geological instability phenomena. This evaluation will give the opportunity to introduce environmental issues into forest planning. |
|---|---|
| Has modelling scope | Forest indicators |
| Has temporal scale | Long term (strategic), Short term (operational) |
| Has spatial context | Spatial with no neighbourhood interrelations |
| Has spatial scale | Forest level, Stand level |
| Has objectives dimension | Multiple objectives |
| Has related DSS | |
| Has goods and services dimension | Market wood products, Non-market services |
| Has decision making dimension | Single decision maker |
| Has forest management goal | multi-functional |
| Supports tree species | all the Italian forest types |
| Supports silvicultural regime | user defined |
Concrete application
| Has typical use case | one forest stand managed at a time |
|---|---|
| Has user profile | |
| Has country | Italy |
| Has references about examples of application | |
| Has number of users | <=10 |
| Has number of real-life applications | <=10 |
| Has utilisation in education | presentation/demo |
| Has research project reference | |
| Has tool dissemination | scientific and technical publications, web site, conferences |
Decision support techniques used in the DSS
| Has decision support techniques | LEaRNForME.Decision support techniques |
|---|
Support of Knowledge Management
| Has knowledge management processes | LEaRNForME.Knowledge management process |
|---|
Support of social participation
| Has support for social participation | LEaRNForME.Support of social participation |
|---|
DSS development
| Has DSS development | LEaRNForME.Description of DSS development |
|---|
Documentation
| Has website | http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm |
|---|---|
| Has online demo | http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm |
| Has manual | Yes |
| Has technical documentation | Yes |
| Has reference | Andrenelli et al., 2007; Scrinzi et al., 2006; Gregori et al., 2007; Scrinzi et al., 2005 |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION (needs to be migrated using the "edit with form" link)
Scope of the system
A procedure has been conceived and implemented in order to support the forester in classifying each homogeneous land unit for:
- predisposition to instability phenomena (termed "propensity") such as shallow landslides, water erosion and runoff generation;
- vegetation cover functionality in contrasting these events.
Both aspects have to be described and modelled by means of distinctive sets of variables; neural network analysis is then applied to a comprehensive set of study cases. The resulting evaluations of predisposition and functionality are combined into four different indexes with descriptive and planning significance:
- equilibrium level, a rough estimation of the balance between tendency and cover protection;
- protection value, assessment of the ability of the vegetation in controlling land degradation;
- constraint level, grade of limitation with respect to timber-oriented management compatible with the assessed protection value;
- action priority, preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices.
At present only the models devoted to the protection from shallow landslides and soil water erosion are operating; analogous procedure for runoff generation is in progress. To try the online-models go to this Web page: http://www.isafa.it/scientifica/assestamento/riselvitalia43/modelli_eng.htm/.
System origin
LEaRNForME was developed during 2001-2007 by Gianfranco Scrinzi, David Galvagni and Giacomo Colle in the Forest Monitoring and Management Unit (Unità di ricerca per il Monitoraggio e la Pianificazione forestale) (http://mpf.entecra.it/) of Italian Council for Research in Agriculture (Consiglio per la Ricerca e la Sperimentazione in Agricoltura) (http://sito.entecra.it).
Support for specific issues
LEaRNForME assists the forestry on site where shallow landslide, water erosion and runoff generation are instability phenomena.
Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type
- Forest planning.
- Territorial planning.
- Protection.
- Prevention.
Capability to support decision making phases
- Intelligence: the system use a fully automatic, congruent, progressive and recordable procedure.
- Design: forest planner input data to evaluate propensity and protective functionality of forest.
- Choice: results give operational and descriptive indexes for sustainable management.
- Monitor: implemented for test areas.
Related systems
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
The typical spatial extent of application is the forest management plan. There isn’t a base spatial unit for the output, it’s depend on what extension data input refer. But the minimum reasonable unit is the forest plot. Definitely we can say that the typical spatial extent of application is the single property scale.
Forest data input
The forest data input are about vegetation cover and forest management disturbances.
Type of information input from user (via GUI)
The user provides basic input data about the site conditions (lithology, aspect, slope, vegetation cover, erodibility, land use, practices, disturbances, etc.). In the shallow landslides model, the users input data to evaluate propensity to instability phenomena concerning: lithology, strata bedding, aspect, slope, climatic aggressiveness, drained area and seismicity. To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data about category of vegetation types, vegetation types, dominating vegetation cover, cover gaps, secondary vegetation cover, forest management disturbances, other disturbances, forest engineering practices, forest engineering practices. In the soil water erosion model the user input data to evaluate the propensity to instability phenomena concerning erodibility, climatic aggressiveness, heat load index, topographic factor. To evaluate vegetation cover protective functionality, the user input data concerning land use categories, land use, dominating vegetational cover, bushes cover, grasses cover, dead materials cover, agro-forest management disturbances, practices, slope.
Models
The system use Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models.
Forest models
Social models
Decision Support
Definition of management interventions
The intersection of the vegetation functionality and land propensity to an instability phenomenon through complex mathematical functions gives four useful indices for soil conservation purposes. The user has to interpret this following indices.
- equilibrium level: this index provides a rough estimation of the balance between land tendency to the analysed geomorphologic phenomenon and cover protection. The “balanced” situation corresponds to conditions of almost equivalent levels of Propensity and Functionality; in these cases one can suppose that the protective action of the vegetation cover is adequate to face the onset of the degradation phenomena under examination. When the warrant provided by the vegetation increases the situation may be classified as “quiet”. On the opposite, the increase of Propensity generates a more or less unbalanced situation which may be defined as “uncertain” or “worrying” according to the algebraic difference between the two indexes;
- protection value: it assesses the ability of the vegetation in controlling land degradation. The protection value is classified into three classes (“high”, “fair” and “negligible”) according to a set of sigmoid functions;
- constraint level: this index expresses the degree of limitation with respect to timber-oriented management in relation to the assessed protection value. The classes of constraint are three: “none or negligible”, allowing the adoption of even very intensive cultural systems; “intermediate”, in which only cutting and harvesting techniques that assure the integrity of root apparatus and soil should be allowed; “maximum”, where only cares devoted to the enhancement of the protective functionality of the vegetation cover should be permitted (woodlands destined primarily to the environmental protection);
- action priority: this index assumes some planning importance by representing a preliminary screening of land units requiring ameliorative practices both for increasing the vegetation cover and for runoff control. The conceptual approach is addressed to prevent the degradation phenomena rather then to reclaim compromised situations. The model provides three classes of “action priority” (“high”, “intermediate” and “negligible”).
Typical temporal scale of application
Planning and operational level.
Types of decisions supported
- Management and sylvicoltural actions.
- Strategic decisions.
- Operating control decisions.
Decision-making processes and models
Output
Types of outputs
The outputs of LEaRNForME Web system are qualitative indices. The outputs of LEaRNForME in stand-alone system are maps and table.
Spatial analysis capabilities
LEaRNForME in stand-alone system integrates weighted overlay capabilities using GIS functions.
Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues
System
System requirements
The Web application runs on multiplatform environment, only an Internet access and a Web browser is required. The stand-alone application requires ArcView 3.x and MS Access.
Architecture and major DSS components
LEaRNForME is both a stand-alone and a Web application. LEaRNForME is a modular system.
Usage
Forest management and planning, educational.
Computational limitations
No limitations for the Web application; in the stand-alone GIS application it depends on hardware and software used.
User interface
The user has to fill the tables for each instability phenomena: in some case he has to select between the proposed values in the pull down menu. It’s not necessary specific computer knowledge for using the system, but geological and forestry comptences is required to choose the appropriate classes for each variable.
Documentation and support
Information about LEaRNForME can be found at the Ri.Selv.Italia project website.
Installation
Installation not needed.
References
Cited references
External resources
- Andrenelli M.C., Colle G., Galvagni D., Giannetti F., Gregori E., Scrinzi G., Zorn G.– Assessing the protective role of the forest cover against hydrogeological disturbances:a GIS-based tool for forest planning - IUFRO International Conference: "NATURAL HAZARDS AND NATURAL DISTURBANCES IN MOUNTAIN FORESTS" - Trento, ITALY (September 18th-21th, 2007);
- Gregori E., Andrenelli M. C., Zorn G., 2007 – Soil and hillslope management using scenario analysis and runoff-erosion models: a critical evaluation of current techniques. International Conference in Florence, ITALY (7th-9th May 2007);
- Andrenelli M. C., Galvagni D., Gregori E., Scrinzi G., Zorn G. Colle G., , 2006 – Propensione all’erosione idrica del suolo: un approccio valutativo in ambiente gis mediante l’utilizzo di reti neurali. - Convegno Nazionale SISS : "Suolo Ambiente Paesaggio", Imola 27-30 giugno 2006;
- Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G. Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2006 – Un modello di valutazione della funzionalità protettiva del bosco per la pianificazione forestale: la componente stabilità dei versanti rispetto ai fenomeni franosi superficiali. Forest@ 3 (1): 98-155;
- Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G., Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2005 - Boschi e fenomeni franosi superficiali: modello per la valutazione dell'azione protettiva. Estimo e Territorio (Ed agricole - il Sole24ore), anno LXVIII - n.12 - dicembre 2005, pp.30-47;
- Scrinzi G., Gregori E., Giannetti F., Galvagni D., Zorn G. Colle G., Andrenelli M. C., 2005 – Un modello di valutazione della funzionalità protettiva del bosco per la pianificazione forestale: la componente stabilità dei versanti rispetto ai fenomeni franosi superficiali., 66 p.
Every documentation about LEaRNForME and research processes can find in the http://www.targetstars.org/ricerca_ex_isafa/riselvitalia43/index_eng.htm