Monsu
General System description
System name: Monsu
Acronym:
Brief overview
Monsu is a calculation and planning software that was developed in Finland in order to be used within multiple-use forestry. It covers scheduling plans generation, numerical optimization and results graphical visualization.
Contents
Scope of the system
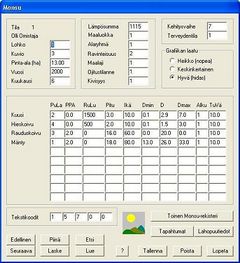
Monsu forest management planning follows three steps [1]:
- Management scheduling
- The forest under planning is divided into compartments, and each compartment is inventoried in the field. The field data (from both living and dead treesare imported to a compartment database. Then, alternative treatment schedules are simulated for the stand compartments. Each treatment schedule is described by treatments attached to it, timber removals, and development of the growing stock characteristics
- Planning model
- For this, Monsu has a planning model writer and various optimisers. The first combines information on decision maker's objectives, and production possibilities of the before simulated treatment schedules of stands. The optimisers can use linear programming and goal programming models, as well as utility theoretic problem formulations, solved with heuristics.
- Solution presentation
- Monsu includes a visual interface and a landscape visualiser to interactive optimisation and also useable after it
System origin
- It was developed by Timo Pukkala and Heikki Parikka
- how was it developed
- Commercial, but inexpensive
- does it have real-life application cases
Support for specific issues
Developed towards a multifunctional forest, Monsu not only estimates timber yields, it also calculates variables describing non-wood forest products and services like berry and mushroom yields, and scenic beauty and recreation scores. Furthermore, so much attention has been paid on its capabilities in ecological planning.
Support for specific thematic areas of a problem type
- Silvicultural
- Certification
- Conservation
- Restoration
- Development choices / land use zoning
- Policy/intervention alternatives
- Sustainability impact assessment (SIA)
Capability to support decision making phases
(NOTE I do not quite know what to do with this, as I do not understand it myself, although it seems related to system use)
(Click here to see a more detailed explanation)
- Intelligence (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Design (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Choice (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
- Monitor (+ explicit description of the support given by the DSS)
Data and data models
Typical spatial extent of application
Forest level.
Forest data input
Inventoried field data are required. Furthermore, not only living trees must be inventoried, also dead trees, because they are considered important for biodiversity.
Type of information input from user (via GUI)
Goals and optimization methods.
Models
Forest models
Timber, berry and mushroom yield models and biodiversity are implemented within Monsu.
Social models
Scenic beauty and recreation scores are taking into account.
Decision Support
Definition of management interventions
At first there is a prescription writer that defines the scheduling possibilities. Then, the user is able to change the weight within the goals proposed in order to reach an available solution.
Typical temporal scale of application
Usually used at tactical level.
Types of decisions supported
- Management level
- strategic decisions
- administrative decisions
- operating control decisions
- Management function
- planning decisions
- organizing decisions
- command decisions
- control decisions
- coordination decisions
- decision making situation
- unilateral
- collegial
- Bargaining / participative decision making
Decision-making processes and models
- Logic modeling
- Operations research modeling
- Direct approaches
- Heuristic manipulation of simulation models
- Business modeling
- Multiple criteria/ranking
Output
Types of outputs
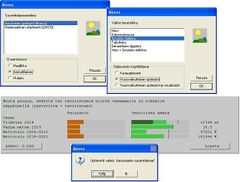
The solution outputs are showed with a visual interface and a landscape visualiser.
Spatial analysis capabilities
Spatial analysis is allowed with the use of the visualization tool, useful for landscape level.
Abilities to address interdisciplinary, multi-scaled, and political issues
Being a multi-use forest management addressed tool, it has the capability of helping to solve ecological, technical, economic and social interactions.
System
System requirements
- Operating Systems: Microsoft Windows OS
- Currently the 4.0 version is the most recent.
Architecture and major DSS components
Describe the basic architecture of the system in software and hardware. Desktop client-server, web based, as well as the integration with available systems. Basic data flow, focusing on retrieval of required input and propagation and implementations of decisions. Mention its modular and scalability capabilities.Usage
It is used for teaching and forest planning at the farm and regional levels in Finland.
Computational limitations
Describe the system limitations: e.g. number of management units, number of vehicles, time horizon
User interface
Describe the quality of user interface and the Prerequisite knowledge for using the system
Documentation and support
Describe the connection to Help-system and possibilities for assistance, as well as the required training and user support levels
Installation
- Prerequisite knowledge: Level of effort to become functional
- Cost: (purchase price, development costs, demonstrated return on investment, cost of use, training costs, licence and maintenance costs)
- Demo: allows the download/utilization of a trial version. If yes, where is it available and what are the trial conditions.
References
Cited references
- ↑ PUKKALA T. 2004. Dealing with Ecological Objectives in the Monsu Planning System. Silva Lusitana. nº especial: 1 - 15.